What Is Health Insurance?
Health insurance is a contract between an individual and an insurance provider that helps cover medical expenses. It provides financial protection against high healthcare costs by sharing the risks of medical bills. A health insurance policy outlines the terms of the coverage, such as what services are included, the costs involved, and how claims are processed.
Key Components of Health Insurance
Premiums
The amount you pay monthly (or annually) to maintain coverage.
Deductibles
The amount you pay out-of-pocket for healthcare services before the insurance company starts covering costs.
Copayments and Coinsurance
- Copayments (Copays): A fixed fee for specific services (e.g., $20 for a doctor visit).
- Coinsurance: A percentage of the cost you pay after meeting your deductible (e.g., 20%).
Out-of-Pocket Maximum
The maximum amount you’ll pay in a year for covered services. Once reached, the insurance covers 100% of costs for the rest of the year.
Health Insurance Policy

A health insurance policy is the official document that outlines the terms of your coverage. It includes:
- The types of medical expenses covered.
- The cost-sharing responsibilities, such as premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket limits.
- The process for filing claims and any exclusions or limits to the coverage. It’s essential to read and understand your policy to know what is covered and what isn’t.
Tips for Choosing a Health Insurance Plan
Assess Your Needs
Consider how often you visit doctors, need prescriptions, or require specialist care.
Understand Your Budget
Balance premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs to find a plan that fits your financial situation.
Check the Network
Ensure your preferred doctors and hospitals are in-network.
Review Covered Services
Look at essential benefits like preventive care, mental health services, and prescriptions.
Know Enrollment Periods
Be aware of open enrollment dates or special enrollment periods triggered by life events.
Why Health Insurance Matters
- Provides financial security against unexpected medical expenses.
- Encourages preventive care to avoid costly health issues.
- Ensures access to quality healthcare and treatments.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
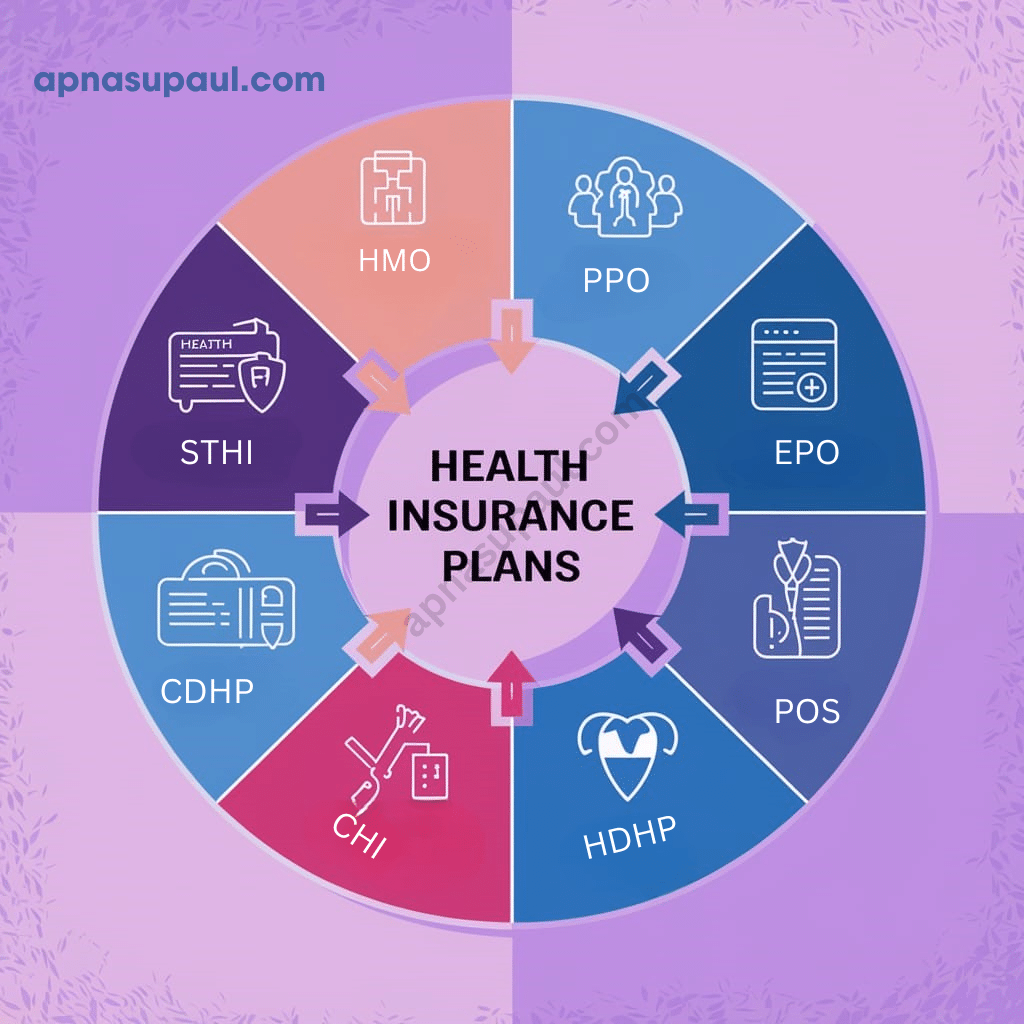
1. Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
- How it works: Requires members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates all healthcare needs and provides referrals to specialists.
- Pros: Lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs, easier to manage care.
- Cons: Limited network of doctors and hospitals, no coverage for out-of-network care except in emergencies.
2. Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
- How it works: Offers more flexibility by allowing members to see any doctor or specialist without a referral, even out-of-network (though at a higher cost).
- Pros: Greater flexibility and choice of healthcare providers, no need for referrals.
- Cons: Higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to HMOs.
3. Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
- How it works: Similar to PPOs but with more restrictions. Members must use the plan’s network of providers, except in emergencies.
- Pros: Lower premiums than PPOs, no need for referrals.
- Cons: No coverage for out-of-network care except in emergencies.
4. Point of Service (POS)
- How it works: Combines elements of HMO and PPO plans. Members choose a primary care physician (PCP) and need referrals to see specialists, but can also go out-of-network at a higher cost.
- Pros: More flexibility than an HMO, lower premiums than PPOs.
- Cons: Requires referrals for specialists, higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care.
5. High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP)
- How it works: Features higher deductibles and lower premiums. Often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) to help manage costs.
- Pros: Lower monthly premiums, can contribute to an HSA for tax benefits.
- Cons: Higher out-of-pocket costs until the deductible is met.
6. Catastrophic Health Insurance
- How it works: Designed for young, healthy individuals or those who cannot afford traditional plans. It covers essential health benefits after high deductibles are met and provides coverage for worst-case scenarios (e.g., serious accidents or illnesses).
- Pros: Very low premiums, protects against major health emergencies.
- Cons: High deductibles, limited coverage for routine healthcare.
7. Consumer-Directed Health Plans (CDHP)
- How it works: Combines high-deductible plans with a tax-advantaged savings account (HSA or Health Reimbursement Account). These plans give individuals more control over healthcare spending.
- Pros: Lower premiums, ability to save money tax-free for medical expenses.
- Cons: High deductibles, more responsibility for managing healthcare costs.
8. Short-Term Health Insurance
- How it works: Provides temporary coverage for individuals who are between plans or need coverage for a short time (up to 12 months or more in some states).
- Pros: Affordable for short-term needs.
- Cons: Limited coverage, may not cover pre-existing conditions, and doesn’t meet ACA (Affordable Care Act) standards.
Also Read: Safeguarding Your Sanctuary: The Unseen Benefits Of Home Insurance